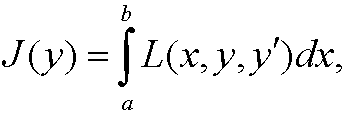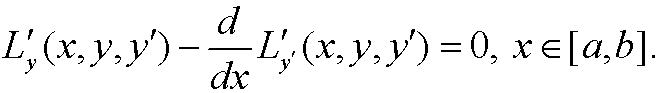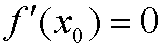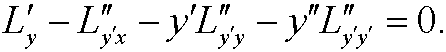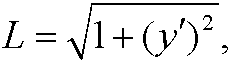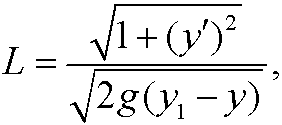5. Euler's equation for the simplest problem.
Theorem 1: If a functiony is extremal to the function
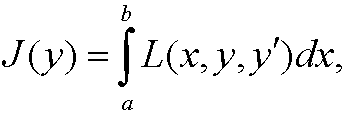 wherey belongs to C2[a,b] and
wherey belongs to C2[a,b] and
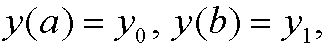 then y must fulfill the Euler equation
then y must fulfill the Euler equation
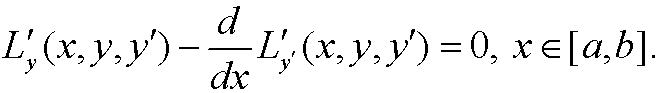 Remark: The Euler equation corresponds to the condition
Remark: The Euler equation corresponds to the condition
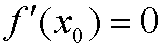 in extreme value problems and is an ordinary differential equation that in general is nonlinear. By using the chain rule, we see that it can be expanded as
in extreme value problems and is an ordinary differential equation that in general is nonlinear. By using the chain rule, we see that it can be expanded as
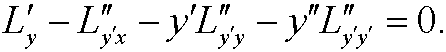 The function L=L(x,y,y‘) is called the Lagrangian of the problem. In our previous problems problems 4, 5 and 6 the Lagrangians were
The function L=L(x,y,y‘) is called the Lagrangian of the problem. In our previous problems problems 4, 5 and 6 the Lagrangians were
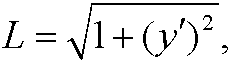
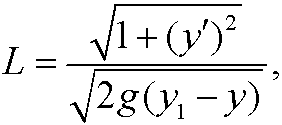
and
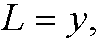 respectively.
respectively.